Medial Tibial Stress Syndrome (MTSS), commonly known as ‘shin splints,’ is a frequently encountered condition in athletes and active individuals. It usually manifests as debilitating leg pain forcing most patients to take harmful painkillers for long durations.
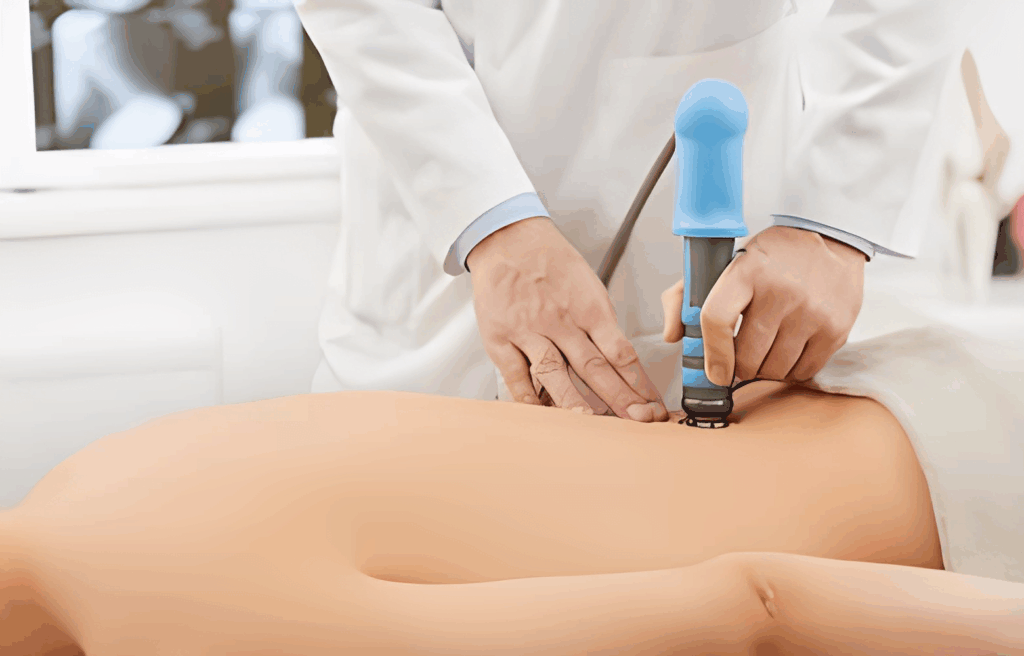
Focal Shockwave Therapy (FST), a non-invasive treatment could be the ideal alternative to help patients deal with this pain. It involves the use of shock waves at injured tissues to help them heal faster, while simultaneously providing relief from inflammatory pain.
Understanding Medial Tibial Stress Syndrome
Medial tibial stress syndrome is characterized by pain along the inner edge of the tibia, triggered by activities like running or jumping. Its exact cause is multifactorial, stemming from overuse, improper footwear, or biomechanical irregularities.
Patients typically report a sharp, throbbing pain during physical activity, which might subside with rest. Diagnosis often involves physical examination and, occasionally, imaging tests to rule out other conditions.
Traditional management includes rest, ice, compression, elevation (RICE), physical therapy, and modifications in activity levels. However, these methods sometimes fall short of providing rapid or effective relief.
Focal Shockwave Therapy
Focal Shockwave Therapy is a non-invasive procedure using acoustic waves to stimulate healing in injured tissues. Initially used for treating kidney stones, it has gained traction in orthopedics for its regenerative capabilities.
It works by delivering focused shockwaves to the affected area, enhancing blood circulation, and accelerating tissue repair and regeneration. This process also reduces inflammation and alleviates pain.
Application of Focal Shockwave Therapy in Treating Medial Tibial Stress Syndrome
Focal Shockwave Therapy (FST) represents a significant leap in the treatment of Medial Tibial Stress Syndrome (MTSS), commonly known as shin splints.
Efficacy in Pain Management and Tissue Repair
- Pain Reduction:
One of the most notable impacts of FST in treating MTSS is its ability to significantly reduce pain. The high-energy acoustic waves effectively stimulate the affected tissue, promoting natural healing processes. This leads to a rapid decrease in pain levels, often noticed by patients after just a few sessions.
- Enhanced Tissue Repair:
FST accelerates the healing process by enhancing blood flow to the affected area. This increased circulation brings more oxygen and nutrients, aiding in the repair of damaged tissue. Additionally, the shockwaves stimulate the formation of new blood vessels, a process known as angiogenesis, which further aids in the healing of the tibial region affected by MTSS.
Clinical Studies and Research Outcomes
Numerous clinical studies have underscored the success of FST in treating MTSS. Studies have demonstrated that patients receiving FST showed a more significant reduction in pain and faster return to full activity compared to those receiving conventional treatments. These studies suggest that FST not only provides immediate relief but also contributes to a more sustainable recovery, reducing the likelihood of MTSS recurrence.
Focal Shockwave Therapy Vs. Conventional Treatments
When compared to traditional methods like rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE), FST or other minimally invasive treatments, it offers several advantages:
- Targeted Treatment: FST directly addresses the pain source, providing more precise and effective treatment compared to general methods like icing or rest.
- Quicker Recovery: Patients undergoing FST often experience a quicker return to their normal activities and sports, an essential factor for athletes and physically active individuals.
- Reduced Dependence on Pain Medication: As FST effectively manages pain and accelerates healing, there is typically a lesser need for pain medication, which can be beneficial for patients concerned about the side effects of long-term medication use.
Customizing FST for Individual Needs
It is important to know that FST is not a one-size-fits-all solution. The treatment should be customized based on the individual’s specific condition, severity of symptoms, and response to initial sessions. Factors like the frequency of therapy, intensity of shockwaves, and the overall number of sessions can be adjusted to optimize outcomes.
Procedure and Implementation
The treatment involves applying a handheld device emitting shockwaves directly to the affected area. Sessions typically last for about 5-10 minutes and may require multiple visits.
Ideal candidates are those who have not responded adequately to conventional treatments. However, FST is not recommended for pregnant women, patients with blood clotting disorders, or those with certain types of bone tumors.
Conclusion
Focal Shockwave Therapy represents a significant advancement in treating Medial Tibial Stress Syndrome, offering a potent blend of efficacy, safety, and convenience. As research evolves, focal shockwave therapy may revolutionize the management of sports-related injuries, promising athletes a faster return to physical health with minimal discomfort.