A rotator cuff tear is a common injury involving the muscles and tendons that stabilize the shoulder joint. It can result from acute trauma or repetitive wear and tear. Treatment options vary depending on the severity of the tear, the patient’s activity level, and overall health. Below is an overview of the available approaches.
Non-Surgical Treatment Options
Non-surgical treatments are typically the first line of defense for partial tears or less severe cases.
- Rest and Activity Modification
Avoiding activities that exacerbate pain can prevent further damage and allow the injury to heal. - Physical Therapy
A tailored exercise program improves strength, flexibility, and range of motion, which may help compensate for a damaged tendon. - Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
Medications such as ibuprofen or naproxen reduce inflammation and alleviate pain. - Corticosteroid Injections
Steroid injections can provide temporary pain relief, particularly for patients with severe inflammation.
Surgical Treatment Options
Surgery may be necessary for full-thickness tears, persistent symptoms, or patients with high functional demands.
- Arthroscopic Surgery
This minimally invasive procedure involves small incisions and the use of a camera to guide repairs, leading to shorter recovery times. - Open Surgery
Traditional open surgery is employed for complex tears or when larger repairs are required. - Mini-Open Repair
Combining arthroscopic techniques with a smaller incision, this approach allows for effective tendon repair with reduced recovery time. - Tendon Transfers
If the rotator cuff tear is irreparable, surgeons may transfer nearby tendons to restore function. - Shoulder Replacement (Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty)
This option is reserved for patients with significant rotator cuff damage combined with arthritis.
Emerging and Alternative Therapies
Innovative treatments continue to evolve for rotator cuff injuries.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
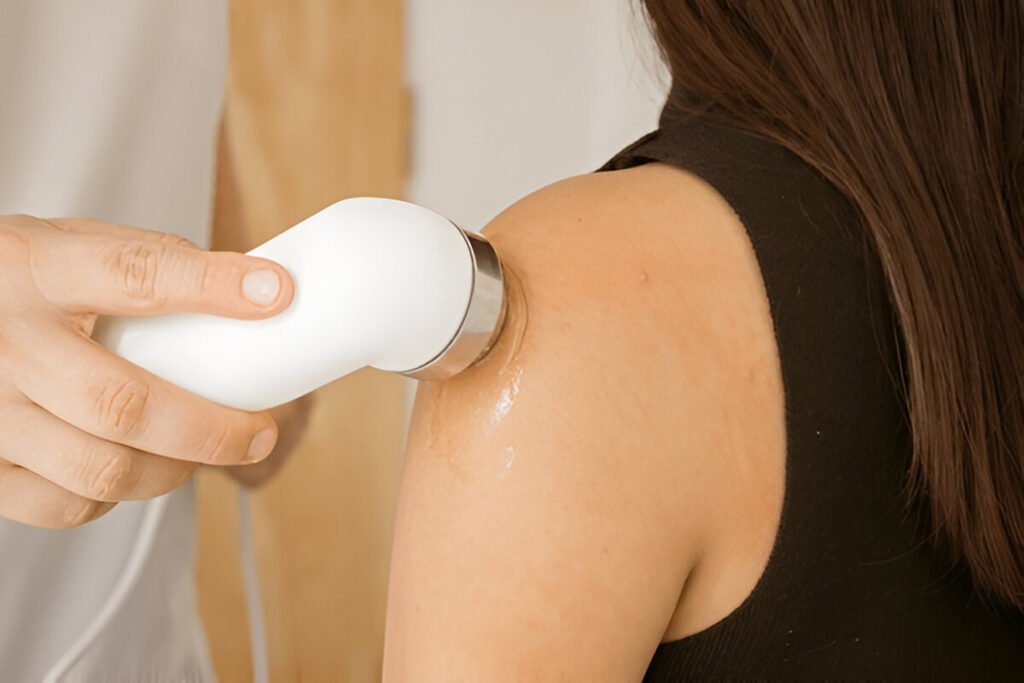
Injecting PRP, derived from the patient’s blood, into the damaged area may promote healing. - Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cells are being explored for their potential to regenerate damaged tissue, although more research is needed. - Shockwave Therapy
High-energy sound waves may stimulate healing and reduce pain in chronic cases.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Regardless of the treatment approach, rehabilitation plays a crucial role in recovery. Physical therapy often begins within weeks of treatment to restore strength and mobility. Patients undergoing surgery may require several months to return to full activity.
Choosing the Right Treatment
The best treatment for a rotator cuff tear depends on various factors, including the extent of the injury, the patient’s goals, and overall health. Consulting a specialist ensures a personalized treatment plan that optimizes outcomes.
Addressing a rotator cuff tear promptly can prevent complications and restore shoulder function, allowing patients to return to their daily activities with minimal pain and limitations.
To learn more about their vein care services, visit MVM Health’s website.