Beyond the Surface: Exploring the Depths of Rib and Back Pain
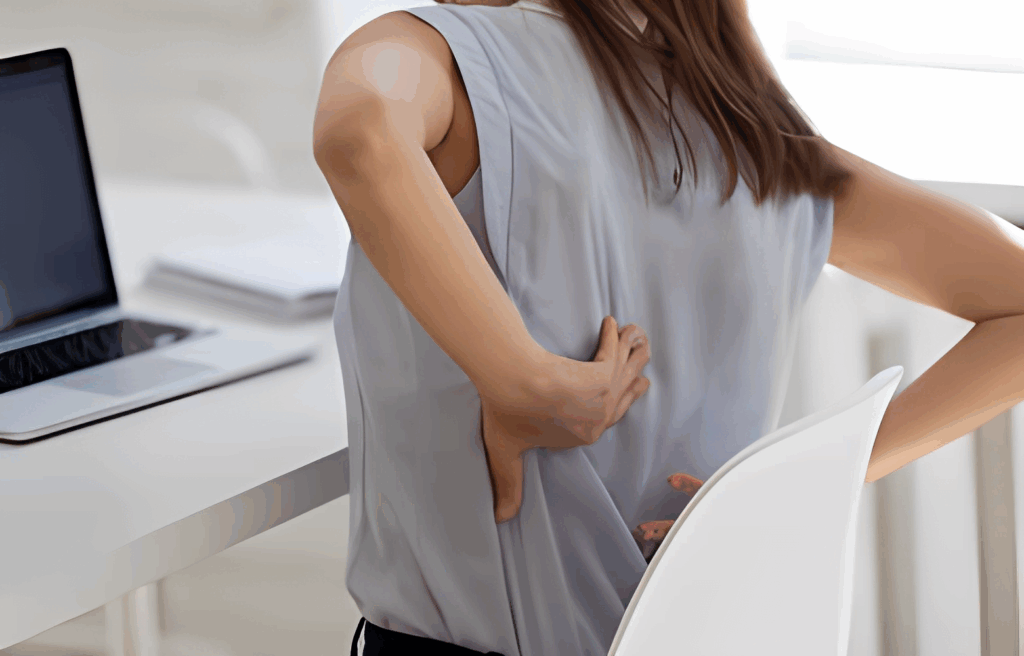
Rib and back pain are pervasive issues that significantly detract from individuals’ quality of life, limiting their daily activities and overall well-being. Commonly, these pains are attributed to straightforward causes like muscle strain or accidental injuries.
However, the reality is that the origins of rib and back pain can be deeply complex, interwoven with a variety of anatomical, psychological, and often overlooked factors. This article delves into these intricate causes, aiming to shed light on the multifaceted nature of these conditions and guide those affected toward effective solutions.
Understanding the Intricacies of Rib and Back Pain
Rib and back pain, though frequently mentioned in tandem, stem from distinct anatomical sources. Rib pain primarily arises from issues within the ribcage itself, such as bone or cartilage afflictions, while back pain is generally related to the muscles, nerves, or vertebral structures.
Symptoms vary widely, ranging from sharp, piercing pain to a persistent dull ache, often exacerbated by specific actions like breathing, coughing, or physical activity. While it’s tempting to pinpoint simple causes such as muscle strains or poor posture, these symptoms can be just the tip of the iceberg, hinting at deeper underlying issues.
Anatomical Insights into Pain
The anatomy of the rib and back regions is complex, with an intricate interplay between bones, muscles, nerves, and other tissues. This complexity is a key factor in why pain occurs, as any dysfunction in these interconnected structures can lead to discomfort or severe pain. Understanding the anatomy is crucial for identifying the true sources of pain, emphasizing the importance of considering the whole system rather than isolated parts.
Internal Causes
Internal organ problems can often present as back pain, misleading those affected and their healthcare providers. Conditions such as kidney stones or cardiac issues may initially manifest as back discomfort, complicating the diagnostic process. Similarly, diseases that directly impact the spine, like osteoporosis or arthritis, contribute to pain, highlighting the need for a thorough medical evaluation to uncover these internal causes.
Psychological and Emotional Factors
The role of stress and emotional well-being in physical pain cannot be overstated. Chronic stress can lead to persistent muscle tension, especially in the back, while psychological health significantly influences pain perception. This connection underscores the necessity of a holistic treatment approach, addressing both the physical symptoms and the mental and emotional health of the individual.
Uncovering Less Common Culprits
Several less common conditions can lead to significant rib and back pain. For example, rib fractures, while identifiable through trauma history and diagnostic imaging, can cause ongoing pain issues. Costochondritis, an inflammation of the rib cage’s cartilage, mimics chest pain often mistaken for heart-related conditions. Scoliosis and other spinal deformities alter spinal alignment, potentially leading to discomfort or pain. Furthermore, visceral referred pain underscores the complexity of diagnosing these conditions, as pain from internal organs may be felt in the back or ribs, further complicating the diagnostic landscape.
The Challenge of Diagnosis
Accurately diagnosing the cause of rib and back pain is fraught with challenges due to the myriad potential sources. A comprehensive medical evaluation is essential, incorporating detailed physical examinations, advanced imaging techniques, and, when necessary, consultations with specialists. This extensive diagnostic approach is critical to ensure that less apparent causes are not overlooked, paving the way for effective treatment.
Navigating Treatment Approaches
Treatment options for rib and back pain vary from conservative measures like physical therapy and medication to more invasive procedures such as surgery. The cornerstone of effective treatment is a customized plan that caters to the individual’s specific diagnosis, needs, and lifestyle. Additionally, the advent of new treatments and therapies offers renewed hope for those dealing with chronic pain, promising more effective relief and improved quality of life.
Strategies for Prevention and Management
Preventing rib and back pain involves making informed lifestyle choices, adopting ergonomic practices, and engaging in regular exercise to strengthen the muscles supporting the back and core. For individuals experiencing chronic pain, adopting long-term management strategies is vital. These strategies focus on maintaining mobility, managing pain levels, and preventing additional injuries, emphasizing the importance of a proactive and comprehensive approach to health.
Conclusion
The journey to understanding and treating rib and back pain is a complex one, necessitating a deep dive into the myriad factors that contribute to these conditions. By exploring beyond the surface causes and considering the anatomical, psychological, and lesser-known factors involved, individuals can pursue a more accurate diagnosis and effective treatment plan.
Embracing a holistic view of health—acknowledging the interconnection of physical, emotional, and mental well-being—is essential in addressing rib and back pain. Professional guidance is crucial in navigating this complex terrain, ensuring a path toward relief and a better quality of life for those affected.