Tendinopathy, a condition marked by tendon pain and functional limitations, poses a significant challenge to people, particularly athletes and those leading active lifestyles. Traditional treatment modalities often offer symptomatic relief but may not address the underlying tissue pathology, leaving a gap in effective management strategies. Shockwave therapy, a non-invasive treatment approach, has garnered attention for its potential to fill this gap, promising not only pain relief but also a pathway to tissue healing.
Understanding Shockwave Therapy
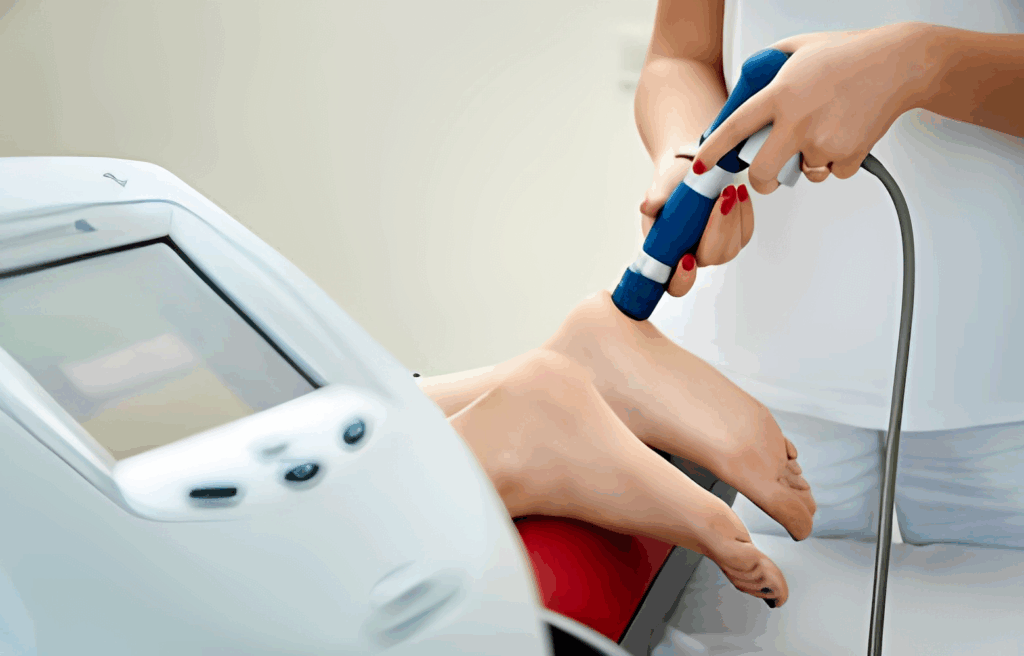
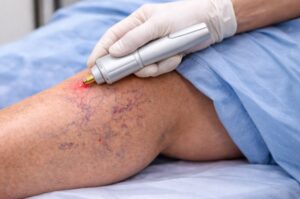
Shockwave therapy, or Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT), involves the application of acoustic waves to affected areas, promoting healing and pain relief. Classified into focused and radial types based on the wave propagation method, this therapy has broadened its application from urological conditions to musculoskeletal disorders, including tendinopathy. The mechanism behind shockwave therapy is its ability to stimulate the body’s natural healing processes, thereby enhancing blood flow and encouraging cellular repair activities.
The Scientific Basis for Shockwave Therapy in Tendinopathy
Tendinopathy disrupts the normal tendon structure, leading to pain and decreased function. Traditional therapies often provide temporary relief, failing to address the cellular degeneration at the heart of the condition. Shockwave therapy, however, targets these underlying issues directly.
By stimulating blood circulation and cellular metabolism, it promotes the repair of damaged tendon fibers and reduces inflammation. Clinical research supports its efficacy, with studies highlighting improved outcomes in pain management and tendon function among patients treated with shockwave therapy compared to those receiving conventional treatments.
Practical Insights into Shockwave Therapy Treatment
Undergoing shockwave therapy typically involves multiple sessions, each lasting a few minutes, with the exact number tailored to the patient’s specific condition. The process is straightforward and does not necessitate anesthesia, facilitating a swift return to daily routines. Despite its benefits, the availability and cost of shockwave therapy can vary, making it important for interested patients to consult with healthcare providers to understand their options.
Benefits of Choosing Shockwave Therapy
Shockwave therapy offers several advantages for those suffering from tendinopathy:
- Pain Management: It provides significant pain relief, often allowing patients to engage in activities that were previously difficult or impossible.
- Tissue Regeneration: The therapy encourages the healing of tendon tissues, aiming to restore their normal function.
- Safety and Non-invasiveness: As a non-surgical treatment option, shockwave therapy presents a lower risk of complications, making it an attractive choice for many patients.
Considering the Risks and Limitations
While shockwave therapy is considered safe for many, it can lead to minor side effects like bruising or temporary discomfort at the treatment site. It’s not universally appropriate, particularly for pregnant people or those with certain health conditions. A thorough consultation with a healthcare professional is essential to evaluate its suitability and potential benefits for each patient.
The Evolving Role of Shockwave Therapy in Musculoskeletal Treatment
The ongoing development of shockwave therapy, fueled by research and technological advancements, suggests a promising future in the treatment of musculoskeletal disorders. Studies continue to explore its mechanisms, aiming to optimize treatment protocols and expand its applicability. The therapy’s potential to become a mainstream treatment for tendinopathy and other conditions is increasingly recognized by the medical community.
Conclusion
Shockwave therapy stands out as an innovative and effective option for managing tendinopathy, offering hope for pain relief and functional recovery without the need for invasive procedures. Its growing evidence base highlights its role in promoting tissue healing, making it a valuable tool in the treatment arsenal for tendon-related issues. Patients considering this therapy should engage in discussions with their healthcare providers to determine its appropriateness for their specific needs, taking into account its potential benefits and limitations.